Drawing Specifications 1.0
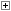 MASSIVE HEAT TREATMENTS
MASSIVE HEAT TREATMENTS  CONVENTIONAL PRELIMINAR MASSIVE HEAT TREATMENTS
CONVENTIONAL PRELIMINAR MASSIVE HEAT TREATMENTS ANNEALINGS
ANNEALINGS Soft annealing
Soft annealing Full annealing
Full annealing Spheroidal annealing
Spheroidal annealing Sub-critical spheroidal annealing
Sub-critical spheroidal annealing Pendular spheroidal annealing
Pendular spheroidal annealing Stress relief annealing
Stress relief annealing NORMALIZING
NORMALIZING Normalizing
Normalizing Normalizing and tempering
Normalizing and tempering Workability quench and tempering
Workability quench and tempering PRELIMINAR ISOTHERMAL MASSIVE HEAT TREATMENTS
PRELIMINAR ISOTHERMAL MASSIVE HEAT TREATMENTS Isothermal annealing
Isothermal annealing Spheroidal isothermal annealing
Spheroidal isothermal annealing CONVENTIONAL FINAL MASSIVE HEAT TREATMENTS
CONVENTIONAL FINAL MASSIVE HEAT TREATMENTS Hardening and stress relief tempering
Hardening and stress relief tempering Hardening and tempering
Hardening and tempering Martempering and stress relief tempering
Martempering and stress relief tempering Stress relief tempering
Stress relief tempering Tempering
Tempering Quench and tempering
Quench and tempering FINAL ISOTHERMAL MASSIVE HEAT TREATMENTS
FINAL ISOTHERMAL MASSIVE HEAT TREATMENTS Isothermal hardening or Bainitic hardening or Austempering or Isothermal quench and tempering
Isothermal hardening or Bainitic hardening or Austempering or Isothermal quench and tempering SELECTIVE HEAT TREATMENTS
SELECTIVE HEAT TREATMENTS  SURFACE HARDENING
SURFACE HARDENING Induction surface hardening and stress relief tempering
Induction surface hardening and stress relief tempering Surface laser hardening ans stress relief tempering
Surface laser hardening ans stress relief tempering Flaming surface hardening and stress relief tempering
Flaming surface hardening and stress relief tempering EBM surface hardening and stress relief tempering
EBM surface hardening and stress relief tempering THERMOCHEMICAL TREATMENTS
THERMOCHEMICAL TREATMENTS  CARBURIZING
CARBURIZING Carburizing, direct hardening and stress relief tempering
Carburizing, direct hardening and stress relief tempering Carburizing, indirect hardening and stress relief tempering
Carburizing, indirect hardening and stress relief tempering Carburizing, double hardening and stress relief tempering
Carburizing, double hardening and stress relief tempering Carburizing, hardening after isothermal maintenance and stress relief tempering
Carburizing, hardening after isothermal maintenance and stress relief tempering CARBONITRIDING
CARBONITRIDING Carbonitriding, direct hardening and stress relief tempering
Carbonitriding, direct hardening and stress relief tempering Nitriding
Nitriding NITROCARBURIZING
NITROCARBURIZING Ferritic nitrocarburizing
Ferritic nitrocarburizing Ferritic nitrocarburizing + oxidation
Ferritic nitrocarburizing + oxidation Ferritic sulphidizing
Ferritic sulphidizing Ferritic sulphidizing + oxidation
Ferritic sulphidizing + oxidation MECHANICAL TREATMENTS
MECHANICAL TREATMENTS  Shot peening
Shot peening SURFACE TREATMENTS
SURFACE TREATMENTS  PHOSPHATION
PHOSPHATION Zinc phosphation
Zinc phosphation Manganese phosphation
Manganese phosphationTreatment: Ferritic nitrocarburizing + oxidation
- Other names: none
- Standard reference: UNI 10931 : 2001
- Conventional Symbol: NcOE
- Smax compounds layer:
- HV1min:
EFFECTIVE HARDENING THICKNESS AND CLASSES
DEFINITION: EFFECTIVE HARDENING THICKNESS IN NITROCARBURIZING
Effective ferritic nitrocarburizing thickness: distance of the external surface of the hardened layer from the point
where his hardness assumes the conventional value of 100 HV more than the core
| Effective hardening thickness classes | nominal values [mm] | min value [mm] | max value [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| NcE1 ( NcOE1; NcSE1; NcSOE1 ) | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.15 |
| NcE2 ( NcOE2; NcSE2; NcSOE2 ) | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.25 |
| NcE3 ( NcOE3; NcSE3; NcSOE3 ) | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.40 |
| NcE4 ( NcOE4; NcSE4; NcSOE4 ) | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.50 |
| NcE5 ( NcOE5; NcSE5; NcSOE5 ) | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.60 |